Elements
Elements are the smallest substance a material is composed of, it cannot be broken down by physical techniques. There are 92 naturally occurring elements found and there are some artificial ones as well. Elements are composed of atoms.
Atoms are the smallest part of a substance taking place in a chemical reaction. These atoms are further composed of three subatomic particles; neutron, proton, and electron.
The atoms may join to form larger molecules. Molecules are composed of 2 or more atoms bonded together. The number of atoms are stated by the atomic symbol of the element such as H2, O2, N2 etc.
Elements are written as a subscript of their name such as Hydrogen as H and Potassium as K. These are the symbols of their respective element. The symbols of metals are written in separate symbols even though the atoms of the metals do not exist as separate atoms.
Some atoms have a different symbol than their names such as sodium has the atomic symbol of Na, and potassium has the atomic symbol of K. This is because the atomic symbols are given after the Italian names of the elements.
Compounds and Mixtures
Compounds are pure substances made up of atoms of different elements. The compounds are not mixtures of elements, the compounds and mixtures have different properties.
Compounds cannot be separated by physical techniques while mixtures can. 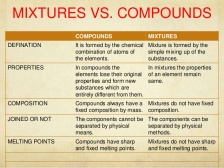 Compounds are also made by chemical processes compared to mixtures. Compounds are written as the combination of the atomic symbol of the elements such as Sodium Chloride has the atomic symbol NaCl. Mixtures are not given atomic symbols.
Compounds are also made by chemical processes compared to mixtures. Compounds are written as the combination of the atomic symbol of the elements such as Sodium Chloride has the atomic symbol NaCl. Mixtures are not given atomic symbols.
For example; if you mix iron filings with sulfur powder, this forms a mixture. Now this can be separated easily if you place a magnet over the mixture. The iron filings will separate from the sulfur powder. If the mixture is heated, it will soon turn red and then turn grey and form a compound called Iron Sulfide.
Forming Bonds
Bonds are formed between atoms to form compounds. Many atoms do not have full electronic configuration. To fill the shells with electrons the atoms tend to form bonds. This can be seen in the elements in Group VIII which are mostly gases. These gases are mainly nonreactive.
This is why they were first known as inert gases. But now many compounds have been found out of these gases and are now known as noble gases. This is because these gases have a full electronic configuration.
Due to having full electronic configuration these gases did not form any compound naturally as no bonding was needed. Although there is still no compound for helium and neon.
Bonding only involves the valence electrons in the outermost shell of the atom of an element while the outer/core electrons are not involved in bonding.
Ionic Bonding
Some elements gain a full electronic configuration by losing electrons and gaining electrons. The ionic bond is formed between an atom which wants to lose an 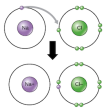 electron and the atom which wants to gain them. The atom which loses the electrons gains a positive charge due to increased number of protons than electrons which produces a cation.
electron and the atom which wants to gain them. The atom which loses the electrons gains a positive charge due to increased number of protons than electrons which produces a cation.
The atom that gains an electron has a negative charge because of increased number of electrons than protons. This forms an anion. These ions form a bond between themselves. This is the result of the electrostatic forces between the cation and the anion. This is why the ionic bonding is also known as electrovalent bonding.
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding is the sharing of electrons. Some elements form compounds this  way mainly because the atoms can not produce sufficient energy for ionic bonding. This why these atoms form covalent bonds. These bonds are represented in words as Cl-Cl, O=O, N≡N etc. These bonds are a result of strong electrostatic forces between the valence electrons and the positively charge nuclei of the atom.
way mainly because the atoms can not produce sufficient energy for ionic bonding. This why these atoms form covalent bonds. These bonds are represented in words as Cl-Cl, O=O, N≡N etc. These bonds are a result of strong electrostatic forces between the valence electrons and the positively charge nuclei of the atom.
Formulae of Compounds
These bonds depend upon the number of electrons needed for a full electronic configuration. These bonds are also dependent upon the combining power of the atoms. The combining power is the amount of atoms an atom of an element can bond with. Such as magnesium has the combining power of 2 and will combine with 2 chlorine atoms to form magnesium chloride.
These bonds are mainly formed from between non metals or metals and nonmetals. Compounds cannot be formed between every element. In case a compounds has a metal in it, its atomic symbol will always be written first and the ending of the nonmetal will be written as “ide” such as oxygen will be written as oxide and chloride will be written as chloride.
Properties of Ionic Bonding
Ionic compounds form a crystal lattice. This means that its structure is fixed in a definite shape. The ions have strong bonds between them which is why ionic compounds tend to have a very high melting and boiling point. The crystal lattice does not allow conductivity as a solid because the ions are not free to move. If the ionic compounds are melted or mixed in a solvent the ions can now move freely and therefore conduct electricity. The ionic compounds are also soluble in water but this does not mean that the soluble compounds are ionic compounds as many such compounds are not soluble in water.
Properties of covalent compounds
Covalent compounds mainly exist as small molecules of compounds. The covalent bonding has intra-molecular forces between them but these tend to have weaker inter-molecular bonds. As a consequence of this these bonds tend to have low boiling point and melting point. Covalent compounds do not have ions and therefore does not conduct electricity.
Many covalent compounds have larger macro-molecules which have large covalent bonds between them. Macromolecules have high melting and boiling points. Some examples are; Silicon dioxide, Silicon Carbide etc.
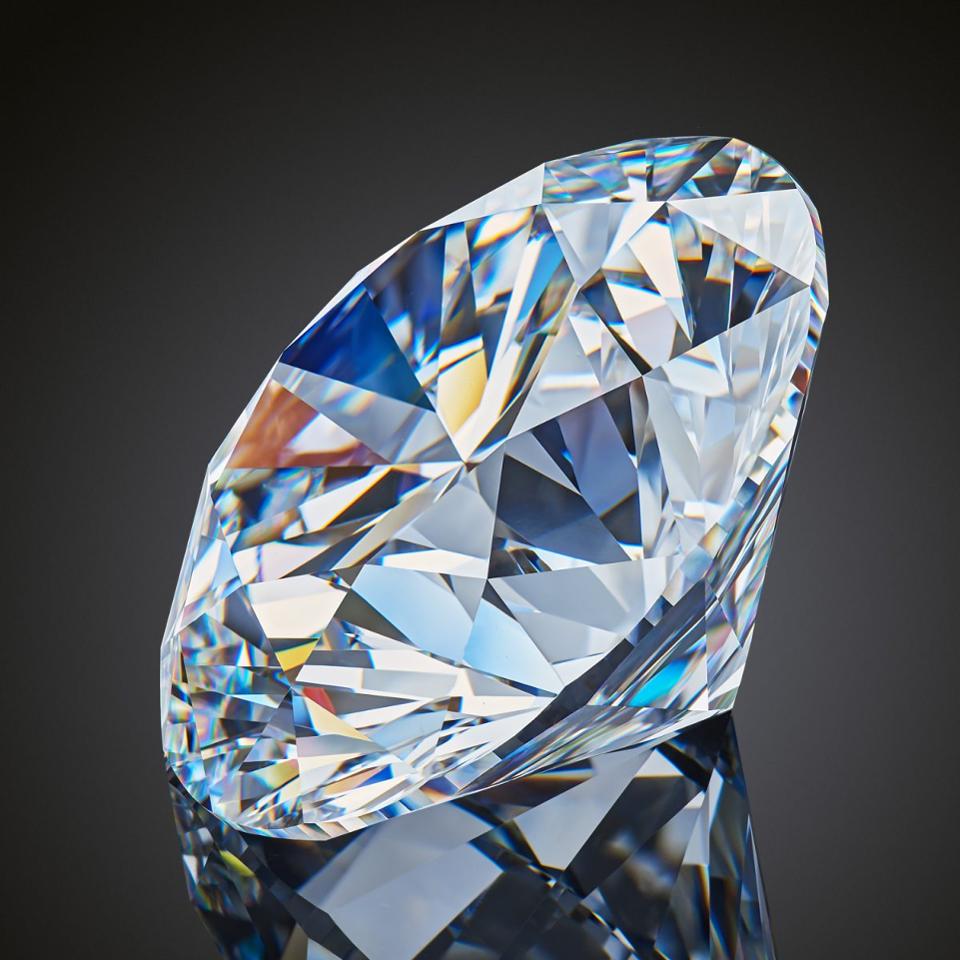
Diamond and Graphite
Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. Allotropes are different structural forms composed of the same element in the same physical state. Diamonds are clear crystals which have covalent bonds between carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded with 4 other carbon atom. Since every atom is set in bonding, there is no valence electron available to conduct electricity, thus it is an insulator. Other than that the diamond has a high refractive index causing the light to refract and brighten up.
 Graphite is also composed of carbon. Each carbon atoms are bonded with 3 other carbon atoms. The atoms form a hexagon. There are valence electrons available in graphite causing it to be a semi conductor. Both diamond and graphite have a very high melting point but other wise each have different properties. Graphite has weak intermolecular bonds thus it can be used as a lubricant whether a solid or mixed in a solvent. It is also used in pencil which is not composed of lead at all. Graphite is comparatively softer material than diamond.
Graphite is also composed of carbon. Each carbon atoms are bonded with 3 other carbon atoms. The atoms form a hexagon. There are valence electrons available in graphite causing it to be a semi conductor. Both diamond and graphite have a very high melting point but other wise each have different properties. Graphite has weak intermolecular bonds thus it can be used as a lubricant whether a solid or mixed in a solvent. It is also used in pencil which is not composed of lead at all. Graphite is comparatively softer material than diamond.
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonds has a lattice of cations with a sea of electrons between them. The electrostatic forces between the valence electrons and the cations forms a very strong bond between the atoms. The valence electrons also result in the metal being a very good conductor.
strong bond between the atoms. The valence electrons also result in the metal being a very good conductor.
Properties of metallic bonds
Metals have valence electrons between their bonds making it a good conductor of heat and electricity. The heat energy agitates the electrons which collide and transfer the heat energy to other ions. Metals are also malleable. The layers of ions tend to fall over each other as the metal is pulled apart.
