Salaam (May God Bless You). Elements are made of atoms which are made of three more subatomic particles which are known as proton, neutron and electron. The word atom is from a Greek word ‘atoms’ which means indivisible. It was proposed by the Greek philosopher, Democritus. He proposed that objects were made by atoms which could not be physically separated. His theory was based on reason and philosophy rather than on scientific experiments.
The Discovery of the Subatomic Particles
Then came John Dalton, an english chemist who in 1808 made several experiments  along with other scientists, to give a description of the atoms. He suggested that atoms were small invisible and indivisible atoms which made up to be elements, atoms are neither created nor destroyed, atoms of same elements are identical and atoms of different elements are different in mass and size and that atoms combine to form compounds in small whole numbers. This was not entirely correct. He gave a supposed structure of the atom to be like a ball.
along with other scientists, to give a description of the atoms. He suggested that atoms were small invisible and indivisible atoms which made up to be elements, atoms are neither created nor destroyed, atoms of same elements are identical and atoms of different elements are different in mass and size and that atoms combine to form compounds in small whole numbers. This was not entirely correct. He gave a supposed structure of the atom to be like a ball.
Then came J.J Thompson. He was experimenting with the cathode rays in 1897, he used a discharge tube which had a cathode and an anode, with two opposite charged electric plates. The discharge tube had inert gas in it which was at low pressure. The discharge tube had a high voltage of about 1500 V. He observed that the cathode rays travelled directly towards the anode and through a small hole travelled further on. It got repelled away by the negatively charged plate and attracted towards the positively charged plate. The
used a discharge tube which had a cathode and an anode, with two opposite charged electric plates. The discharge tube had inert gas in it which was at low pressure. The discharge tube had a high voltage of about 1500 V. He observed that the cathode rays travelled directly towards the anode and through a small hole travelled further on. It got repelled away by the negatively charged plate and attracted towards the positively charged plate. The  cathode rays usually end up travelling straight without the plates. He had discovered the electrons. He then test with other gases at low pressures as well and gave following conclusions after a few more experiments; The cathode rays must be negatively charged as it got repelled by the negatively charged plate but attracted towards the positively charged plate.The cathode rays must carry a charge as they got deflected by both the magnetic and electric field. The particles present in the cathode rays must be present in all atoms. Thompson then provided another model of the atom, saying that atoms had electrons in them but since they are neutral the rest of the mass must be positive. He also identified the mass of the electrons to be the same as always.
cathode rays usually end up travelling straight without the plates. He had discovered the electrons. He then test with other gases at low pressures as well and gave following conclusions after a few more experiments; The cathode rays must be negatively charged as it got repelled by the negatively charged plate but attracted towards the positively charged plate.The cathode rays must carry a charge as they got deflected by both the magnetic and electric field. The particles present in the cathode rays must be present in all atoms. Thompson then provided another model of the atom, saying that atoms had electrons in them but since they are neutral the rest of the mass must be positive. He also identified the mass of the electrons to be the same as always.
The scientist from New Zealand, Ernest Rutherford along with his students Geiger and Marsden discovered the proton in 1910. He had set up a fluorescent sheet around a  thin gold sheet and an alpha particle emitter. He bombarded the gold sheet with alpha particles and observed parts of the fluorescent sheet glow. The glowing points indicated the path taken by the alpha particles. He noticed that a lot of the alpha particles went straight through the gold sheet to reach the fluorescent sheet directly behind the gold sheet but some were at an angle away from the straight path and some were completely repelled backwards. He deduced that the alpha particles had passed through empty space which made up the nucleus of the
thin gold sheet and an alpha particle emitter. He bombarded the gold sheet with alpha particles and observed parts of the fluorescent sheet glow. The glowing points indicated the path taken by the alpha particles. He noticed that a lot of the alpha particles went straight through the gold sheet to reach the fluorescent sheet directly behind the gold sheet but some were at an angle away from the straight path and some were completely repelled backwards. He deduced that the alpha particles had passed through empty space which made up the nucleus of the atom and that there must be a subatomic particle with a positive charge which repelled the alpha particles. Those which were deflected backwards must have come in direct contact with the proton. He then proposed a new model for the atomic structure.
atom and that there must be a subatomic particle with a positive charge which repelled the alpha particles. Those which were deflected backwards must have come in direct contact with the proton. He then proposed a new model for the atomic structure.
In 1932, Chadwick discovered the neutron and made the understanding of the atomic structure much more clearer. He bombarded alpha particles on to materials like  beryllium and saw that it emitted rays like the gamma rays which were extremely penetrating but were not deflected in the magnetic and the electric field making this clear that these rays were neutral. He had discovered neutron and made many conclusions with this.
beryllium and saw that it emitted rays like the gamma rays which were extremely penetrating but were not deflected in the magnetic and the electric field making this clear that these rays were neutral. He had discovered neutron and made many conclusions with this.
Then in 1913, Henry Moseley conducted experiments. He bombarded metals with cathode rays which produced X-rays. He observed that as the mass of the metals increased the wavelength of the X-rays increased as well and the square root of the frequency of the waves was half the atomic mass of the metals. This was the proton number of the elements.

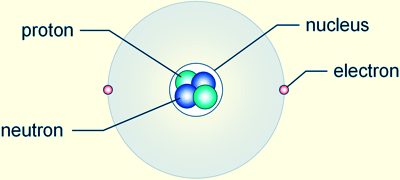 negatively charged subatomic particles which are found in the shells of the atom. The neutrons and protons are found in the nucleus of the atoms. Protons have a positive charge while neutrons carry no charge. Since atoms are not charged particles, that means that the number of protons and electrons are same.
negatively charged subatomic particles which are found in the shells of the atom. The neutrons and protons are found in the nucleus of the atoms. Protons have a positive charge while neutrons carry no charge. Since atoms are not charged particles, that means that the number of protons and electrons are same.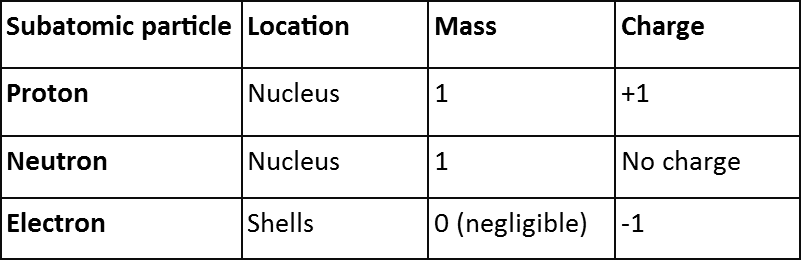 The mass of protons and neutrons are greater than electrons. If the mass of proton is 1 then the mass of electron is taken 0. Even though these two subatomic particles are different in masses they carry a same charge.
The mass of protons and neutrons are greater than electrons. If the mass of proton is 1 then the mass of electron is taken 0. Even though these two subatomic particles are different in masses they carry a same charge.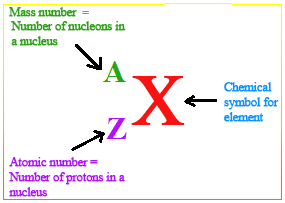
 duplet. The 2nd shell holds 8 electrons forming an octect. The 3rd can hold 18 and the fourth can hold up to 32. If these limits are crossed then the electrons are to be placed in the next shell. However calcium and potassium are free of such pattern because as their 3rd shells exceed 8 electrons it is placed in another shell.
duplet. The 2nd shell holds 8 electrons forming an octect. The 3rd can hold 18 and the fourth can hold up to 32. If these limits are crossed then the electrons are to be placed in the next shell. However calcium and potassium are free of such pattern because as their 3rd shells exceed 8 electrons it is placed in another shell.